注意
本示例与Gymnasium 1.2.0版本兼容。
使用REINFORCE训练Mujoco¶

本教程使用神经网络为MuJoCo环境实现REINFORCE。
我们将使用REINFORCE,它是最早的策略梯度方法之一。与首先学习价值函数再从中推导出策略的繁重任务不同,REINFORCE直接优化策略。换句话说,它被训练来最大化蒙特卡洛回报的概率。稍后会详细介绍。
倒立摆 (Inverted Pendulum) 是Mujoco中的倒立摆,但现在由Mujoco物理模拟器驱动——这允许进行更复杂的实验(例如改变重力效应)。这个环境涉及一个可以线性移动的推车,推车一端固定着一个杆子,另一端自由。推车可以左右推动,目标是通过对推车施加力来使杆子在推车顶部保持平衡。有关环境的更多信息可以在https://gymnasium.org.cn/environments/mujoco/inverted_pendulum/找到。
训练目标:使杆子(倒立摆)在推车顶部保持平衡
动作:智能体采取一个一维向量作为动作。动作空间是一个连续的(action)在[-3, 3]之间,其中action代表施加到推车上的数值力(幅度表示力的大小,符号表示方向)
方法:我们使用PyTorch从头开始编写REINFORCE代码,以训练一个神经网络策略来掌握倒立摆任务。
Gymnasium v0.26+ Env.step() 函数的解释
env.step(A) 允许我们在当前环境“env”中采取动作“A”。环境随后执行该动作并返回五个变量:
next_obs:这是智能体采取动作后将收到的观测值。
reward:这是智能体采取动作后将获得的奖励。
terminated:这是一个布尔变量,表示环境是否已终止。
truncated:这也是一个布尔变量,表示回合是否因提前截断而结束,即达到时间限制。
info:这是一个字典,可能包含有关环境的附加信息。
from __future__ import annotations
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.distributions.normal import Normal
import gymnasium as gym
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (10, 5)
策略网络¶
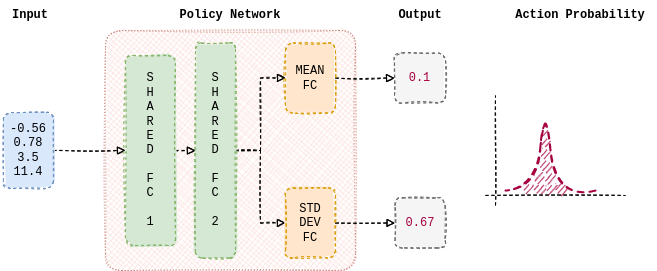
我们首先构建一个策略,智能体将使用REINFORCE来学习它。策略是从当前环境观测到动作概率分布的映射。本教程中使用的策略由神经网络参数化。它由两个线性层组成,这些层在预测的均值和标准差之间共享。此外,单独的线性层用于估计均值和标准差。nn.Tanh在隐藏层之间用作非线性函数。以下函数估计正态分布的均值和标准差,从中采样动作。因此,策略有望学习适当的权重,根据当前观测输出均值和标准差。
class Policy_Network(nn.Module):
"""Parametrized Policy Network."""
def __init__(self, obs_space_dims: int, action_space_dims: int):
"""Initializes a neural network that estimates the mean and standard deviation
of a normal distribution from which an action is sampled from.
Args:
obs_space_dims: Dimension of the observation space
action_space_dims: Dimension of the action space
"""
super().__init__()
hidden_space1 = 16 # Nothing special with 16, feel free to change
hidden_space2 = 32 # Nothing special with 32, feel free to change
# Shared Network
self.shared_net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(obs_space_dims, hidden_space1),
nn.Tanh(),
nn.Linear(hidden_space1, hidden_space2),
nn.Tanh(),
)
# Policy Mean specific Linear Layer
self.policy_mean_net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(hidden_space2, action_space_dims)
)
# Policy Std Dev specific Linear Layer
self.policy_stddev_net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(hidden_space2, action_space_dims)
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
"""Conditioned on the observation, returns the mean and standard deviation
of a normal distribution from which an action is sampled from.
Args:
x: Observation from the environment
Returns:
action_means: predicted mean of the normal distribution
action_stddevs: predicted standard deviation of the normal distribution
"""
shared_features = self.shared_net(x.float())
action_means = self.policy_mean_net(shared_features)
action_stddevs = torch.log(
1 + torch.exp(self.policy_stddev_net(shared_features))
)
return action_means, action_stddevs
构建智能体¶

现在我们已经完成了策略的构建,接下来让我们开发REINFORCE,它赋予策略网络生命。REINFORCE的算法可以在上方找到。如前所述,REINFORCE旨在最大化蒙特卡洛回报。
趣闻:REINFORCE是“‘RE’ward ‘I’ncrement ‘N’on-negative ‘F’actor times ‘O’ffset ‘R’einforcement times ‘C’haracteristic ‘E’ligibility”的首字母缩写。
注:超参数的选择是为了训练一个表现不错的智能体。没有进行广泛的超参数调优。
class REINFORCE:
"""REINFORCE algorithm."""
def __init__(self, obs_space_dims: int, action_space_dims: int):
"""Initializes an agent that learns a policy via REINFORCE algorithm [1]
to solve the task at hand (Inverted Pendulum v4).
Args:
obs_space_dims: Dimension of the observation space
action_space_dims: Dimension of the action space
"""
# Hyperparameters
self.learning_rate = 1e-4 # Learning rate for policy optimization
self.gamma = 0.99 # Discount factor
self.eps = 1e-6 # small number for mathematical stability
self.probs = [] # Stores probability values of the sampled action
self.rewards = [] # Stores the corresponding rewards
self.net = Policy_Network(obs_space_dims, action_space_dims)
self.optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(self.net.parameters(), lr=self.learning_rate)
def sample_action(self, state: np.ndarray) -> float:
"""Returns an action, conditioned on the policy and observation.
Args:
state: Observation from the environment
Returns:
action: Action to be performed
"""
state = torch.tensor(np.array([state]))
action_means, action_stddevs = self.net(state)
# create a normal distribution from the predicted
# mean and standard deviation and sample an action
distrib = Normal(action_means[0] + self.eps, action_stddevs[0] + self.eps)
action = distrib.sample()
prob = distrib.log_prob(action)
action = action.numpy()
self.probs.append(prob)
return action
def update(self):
"""Updates the policy network's weights."""
running_g = 0
gs = []
# Discounted return (backwards) - [::-1] will return an array in reverse
for R in self.rewards[::-1]:
running_g = R + self.gamma * running_g
gs.insert(0, running_g)
deltas = torch.tensor(gs)
log_probs = torch.stack(self.probs).squeeze()
# Update the loss with the mean log probability and deltas
# Now, we compute the correct total loss by taking the sum of the element-wise products.
loss = -torch.sum(log_probs * deltas)
# Update the policy network
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
# Empty / zero out all episode-centric/related variables
self.probs = []
self.rewards = []
现在让我们使用REINFORCE来训练策略,以掌握倒立摆任务。
以下是训练过程的概述:
- 对于每个随机种子
重新初始化智能体
- 对于最大回合数范围内的每个回合
- 直到回合结束
根据当前观测采样动作
执行动作并获得奖励和下一个观测
存储所采取的动作、其概率和观测到的奖励
更新策略
注意:深度强化学习在许多常见用例中对随机种子相当敏感 (https://spinningup.openai.com/en/latest/spinningup/spinningup.html)。因此,测试各种种子非常重要,我们将会这样做。
# Create and wrap the environment
env = gym.make("InvertedPendulum-v4")
wrapped_env = gym.wrappers.RecordEpisodeStatistics(env, 50) # Records episode-reward
total_num_episodes = int(5e3) # Total number of episodes
# Observation-space of InvertedPendulum-v4 (4)
obs_space_dims = env.observation_space.shape[0]
# Action-space of InvertedPendulum-v4 (1)
action_space_dims = env.action_space.shape[0]
rewards_over_seeds = []
for seed in [1, 2, 3, 5, 8]: # Fibonacci seeds
# set seed
torch.manual_seed(seed)
random.seed(seed)
np.random.seed(seed)
# Reinitialize agent every seed
agent = REINFORCE(obs_space_dims, action_space_dims)
reward_over_episodes = []
for episode in range(total_num_episodes):
# gymnasium v26 requires users to set seed while resetting the environment
obs, info = wrapped_env.reset(seed=seed)
done = False
while not done:
action = agent.sample_action(obs)
# Step return type - `tuple[ObsType, SupportsFloat, bool, bool, dict[str, Any]]`
# These represent the next observation, the reward from the step,
# if the episode is terminated, if the episode is truncated and
# additional info from the step
obs, reward, terminated, truncated, info = wrapped_env.step(action)
agent.rewards.append(reward)
# End the episode when either truncated or terminated is true
# - truncated: The episode duration reaches max number of timesteps
# - terminated: Any of the state space values is no longer finite.
#
done = terminated or truncated
reward_over_episodes.append(wrapped_env.return_queue[-1])
agent.update()
if episode % 1000 == 0:
avg_reward = int(np.mean(wrapped_env.return_queue))
print("Episode:", episode, "Average Reward:", avg_reward)
rewards_over_seeds.append(reward_over_episodes)
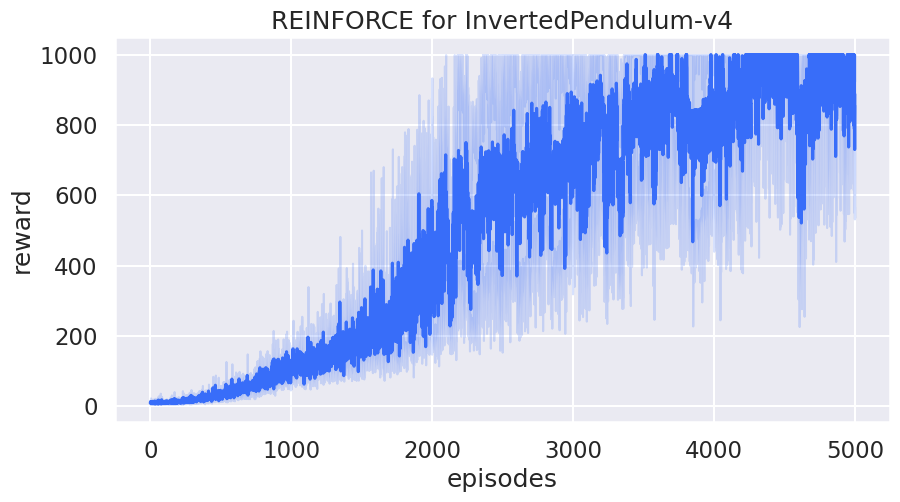
绘制学习曲线¶
df1 = pd.DataFrame(rewards_over_seeds).melt()
df1.rename(columns={"variable": "episodes", "value": "reward"}, inplace=True)
sns.set(style="darkgrid", context="talk", palette="rainbow")
sns.lineplot(x="episodes", y="reward", data=df1).set(
title="REINFORCE for InvertedPendulum-v4"
)
plt.show()
作者:Siddarth Chandrasekar
许可:MIT许可证
参考文献¶
[1] Williams, Ronald J.. “Simple statistical gradient-following algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning.” Machine Learning 8 (2004): 229-256.


